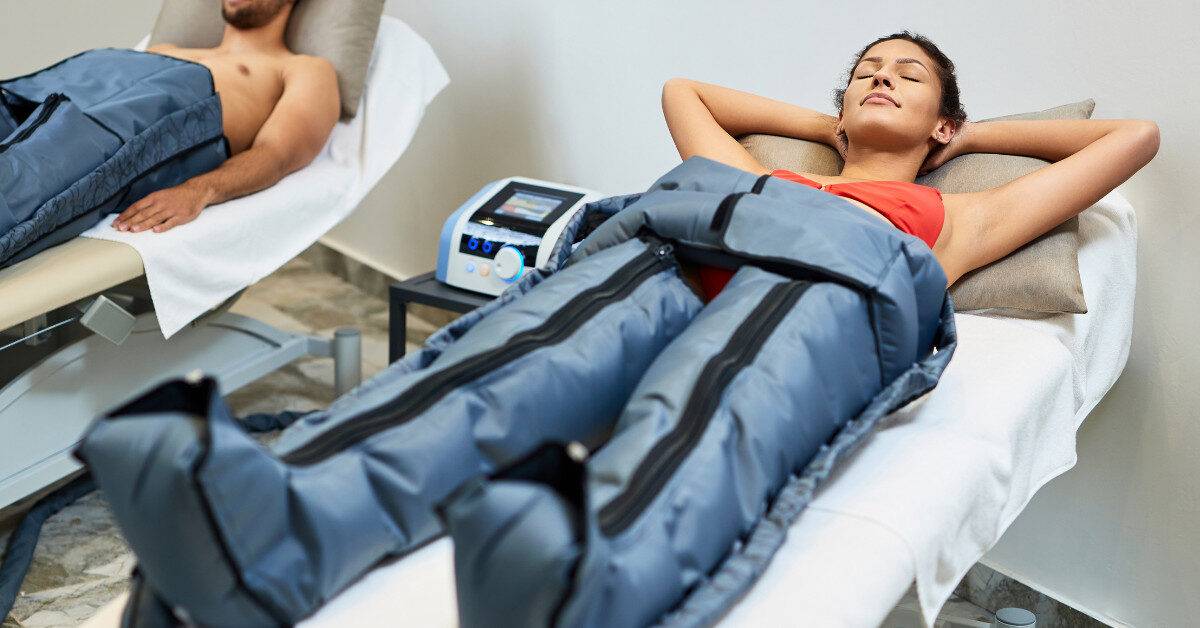
Compression therapy is a clinically-proven method widely used in medical and wellness settings to improve blood flow, reduce swelling, and support recovery from various conditions. Whether you’re managing a venous disorder or recovering after an intense workout, understanding when to use compression therapy and when to avoid it is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore the optimal uses, potential risks, and essential considerations for safe and effective application.
What Is Compression Therapy?
Compression therapy involves applying controlled pressure to the limbs using garments such as compression stockings, bandages, or pneumatic devices. This pressure helps improve venous return, supports lymphatic drainage, and reduces edema. It is a cornerstone in managing venous and lymphatic disorders and has applications in sports medicine and post-operative care.
The therapy works by compressing the surface veins, arteries, and muscles, forcing blood through narrower channels. This helps improve circulation and prevent blood pooling, especially in the lower extremities.
When to Use Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is highly beneficial for various conditions when applied correctly and under appropriate supervision. Here are some key situations where its use is recommended:
Venous Disorders
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI)
- Varicose veins
- Venous ulcers
Lymphedema
- Both primary and secondary types
- Helps manage swelling and prevent fluid buildup
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prevention
- Post-surgery recovery
- Long-haul flights or bed rest
Orthostatic Hypotension
- Prevents dizziness caused by standing due to blood pooling
Athletic and Post-Exercise Recovery
- Reduces swelling and muscle soreness
In each of these conditions, compression therapy promotes faster healing, reduces discomfort, and can significantly improve quality of life.
When to Avoid Compression Therapy
Despite its numerous benefits, compression therapy is not suitable for everyone. There are specific conditions where it could cause harm if not properly managed. At MG Sports Massage, we prioritize safety and patient education, ensuring every client receives appropriate care based on their medical history and individual needs.
Contraindications Include:
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD): Particularly with ABI < 0.5
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF): Can worsen fluid retention
- Acute Skin Infections: Like cellulitis or infected ulcers
- Severe Peripheral Neuropathy: Loss of sensation may mask injury
- Allergies to Compression Materials: Skin irritation or allergic reactions
If you fall into any of these categories, it is essential to consult with a medical professional before starting compression therapy.
Risk Assessment Before Compression Therapy
Before recommending compression therapy, professionals typically perform assessments to ensure it’s safe and effective. One of the most common tools used is the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) test, which measures blood flow and identifies arterial blockages.
Other diagnostic methods include:
- Doppler ultrasound for vein health
- Physical exams to determine the cause of edema
- Review of medical history and current medications
These assessments ensure that compression therapy enhances recovery without compromising circulatory health.
Adjusting Therapy for Individual Needs
No two individuals are alike when it comes to therapy needs. Compression garments come in various pressure levels, typically measured in mmHg. The levels include:
- Class I (15-20 mmHg): Mild support
- Class II (20-30 mmHg): Moderate compression
- Class III (30-40 mmHg): Severe venous conditions
- Class IV (40+ mmHg): Only under strict medical supervision
Adjustments depend on age, activity level, medical condition, and comfort. Custom-fit garments may be necessary for people with unique limb shapes or size differences. Proper training in how to wear and remove compression garments is also essential for safety and efficacy.
Special Considerations for Certain Populations
Some individuals require extra care when considering compression therapy. This includes:
- Elderly patients: May have fragile skin or underlying health issues
- People with diabetes: Risk of peripheral neuropathy
- Pregnant individuals: Hormonal changes and pressure on veins
- Post-operative patients: To reduce DVT risk and enhance healing
Tailored care plans should always be developed for these populations, often in consultation with both healthcare providers and wellness professionals.
Clinical Guidelines and Best Practices
Professional medical bodies like the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum provide detailed guidelines on the use of compression therapy. These outline:
- Proper assessment techniques
- Contraindications and precautions
- Recommended durations and compression classes
For businesses like MG Sports Massage, adhering to these standards ensures safe and effective care. For more information or to check our reviews and ratings, visit our Google Business Profile.
Patient Education: Key to Compliance and Success
One of the most important factors in the success of compression therapy is patient compliance. Without proper education, many patients abandon the therapy due to discomfort or difficulty in application.
Tips for Patients:
- Always follow instructions for wearing and removing garments
- Never sleep with compression stockings unless advised
- Monitor for signs of numbness, discoloration, or pain
- Clean garments regularly and replace as needed
- Schedule follow-ups for reassessment
Empowering patients with knowledge improves outcomes and builds trust in the therapeutic process.
Contact Us
Interested in learning more about compression therapy or booking a consultation?
MG Sports Massage is here to help you determine if compression therapy is right for you. Reach out today to schedule your appointment with our experienced professionals and start your journey toward better health and recovery.
Final Thoughts
Compression therapy offers a multitude of benefits when used appropriately and with medical guidance. It can relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and support long-term wellness. However, it is not suitable for everyone and must be applied with care and consideration.
If you’re considering compression therapy, consult a qualified practitioner who can assess your needs and guide you through the process. At MG Sports Massage, we take a personalized approach to ensure your therapy is both safe and effective.